-
Mems Mirror
Issues Related to Mems Mirror
-
What is MEMS technology?
MEMS (Microelectromechanical Systems) technology represents a manufacturing process that creates microstructures ranging from nanometers to millimeters in scale. This method originated from semiconductor and microelectronics practices. It integrates various modern fabrication techniques such as photolithography, epitaxy, thin-film deposition, oxidation, diffusion, ion implantation, sputtering, evaporation, etching, dicing, and packaging to produce complex three-dimensional micro devices. Essentially, it miniaturizes mechanical systems. MEMS technology not only extensively contributes to micro-device manufacturing but also drives advancements in miniaturization, integration, and smart technologies, leading to revolutionary changes across various fields.
-
What are the operating principles of MExpert's MEMS Mirror?
From a functional perspective, MExpert's MEMS mirror operates in two states: quasi-static and resonant mode.
In quasi-static mode, the control of the mirror surface remains relatively flexible, enabling it to hold stationary at any angle for any duration within a specified frequency. When combined with various wavelengths of laser, it can be applied in fields like laser communications, vector scanning imaging, and spatial light modulation.
In resonant mode, the mirrors achieve a broader range of deflection angles and faster scanning frequencies, approximately equal to the resonant frequency of the MEMS mirror. By adjusting certain control signal parameters in the resonant state, one can produce Lissajous figures. This mode is commonly utilized in projection and imaging applications requiring rapid laser scanning at large angles.
-
What are the key performance indicators of MEMS mirrors ?
The main performance indicators of the MEMS Mirror are: mirror diameter, resonance frequency, and mechanical tilt angle.
-
What distinguishes the piezoelectric MEMS micro-mirror launched by MExpert from other MEMS Mirror?
Compared to the electrostatic and electromagnetic MEMS mirrors on the market, MExpert's piezoelectric MEMS mirrors are high-frequency, large-angle vibrating devices based on novel piezoelectric film technology. These products offer significant advantages, including wide angles, high reliability, resistance to fatigue, low susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, and strong stability.
-
-
Fast Steering Mirror
Concerns Related to Fast Steering Mirror (FSM)
-
What is a fast steering mirror?
Fast Steering Mirror (FSM) serves a primary function: it adjusts the beam's direction by precisely controlling the mirror surface’s orientation. This type of mirror boasts low inertia, easy installation, swift response, and high positioning accuracy. As a result, it finds extensive use in optical systems like astronomical telescopes, space laser communications, and precision targeting.
-
What sizes are available for MExpert's FSM?
MExpert's FSM come in various diameters: 5mm, 8mm, 10mm, and 15mm.
-
What are the main advantages of MEMS FSM compared to traditional FSM?
MEMS FSM are compact, lightweight, energy-efficient, and exhibit high linearity without hysteresis or creep effects.
-
What are the main performance indicators for a FSM surface shape profile?
The primary metrics for the surface shape of MEMS FSM are typically represented by PV values and RMS values. In the realm of long-distance laser communication, the surface shape of the FSM is held to stringent standards, generally requiring the RMS value to be a fraction, specifically one-tenth, of the communication wavelength.
-
What is the lifespan of MEMS fast steering mirrors?
Currently, MEMS Mirror have undergone over 20 billion full-range lifespan tests, demonstrating no significant degradation.
-
What differentiates the MExpert's piezoelectric MEMS fast steering mirror from other traditional fast steering mirrors?
Currently available fast steering mirrors predominantly made of piezoelectric ceramics and voice coil motor . In contrast, the MExpert's piezoelectric MEMS fast steering mirrors are significantly more compact, measuring just 1/8th the size, 1/18th the weight, and requiring only 1/12th the power of traditional fast steering mirrors. This translates to substantial reductions in satellite launch costs and operational power for applications in laser communication satellites, presenting a notable advantage.
-
-
Driver
How to Operate A MExpert's FSM?
-
How to operate a FSM?
Fast steering mirror products are driven by piezoelectric actuation, characterized by low current and high voltage requirements. It is necessary to equip a boost converter to elevate the supply voltage to approximately 120V, while utilizing a high-voltage amplification circuit for actuation. Recommended high-voltage operational amplifiers include OPA462 and ADHV4702. Depending on the type of power supply (dual polarity/single-ended), three distinct connection structures are advised.
Note: Method three for driving only provides a voltage dynamic range of VDD/2.

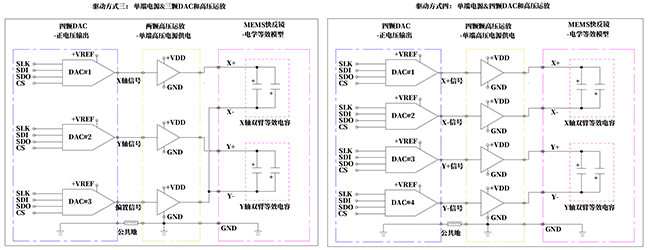
-
What should one do if providing dual voltage is not feasible for driving the FSM?
When requesting samples, please specify the available positive voltage range. MExpert will adjust the connection sequence to ensure the FSM operates within the positive voltage range.
-
Other questions?
We have a professional team with rich experience and profound expertise. We are ready to provide you with comprehensive support and solutions






